A recent article published in the journal Buildings underscores the urgent need to integrate resource efficiency and circular economy principles into the construction sector, given the substantial environmental and socio-economic impacts of buildings.
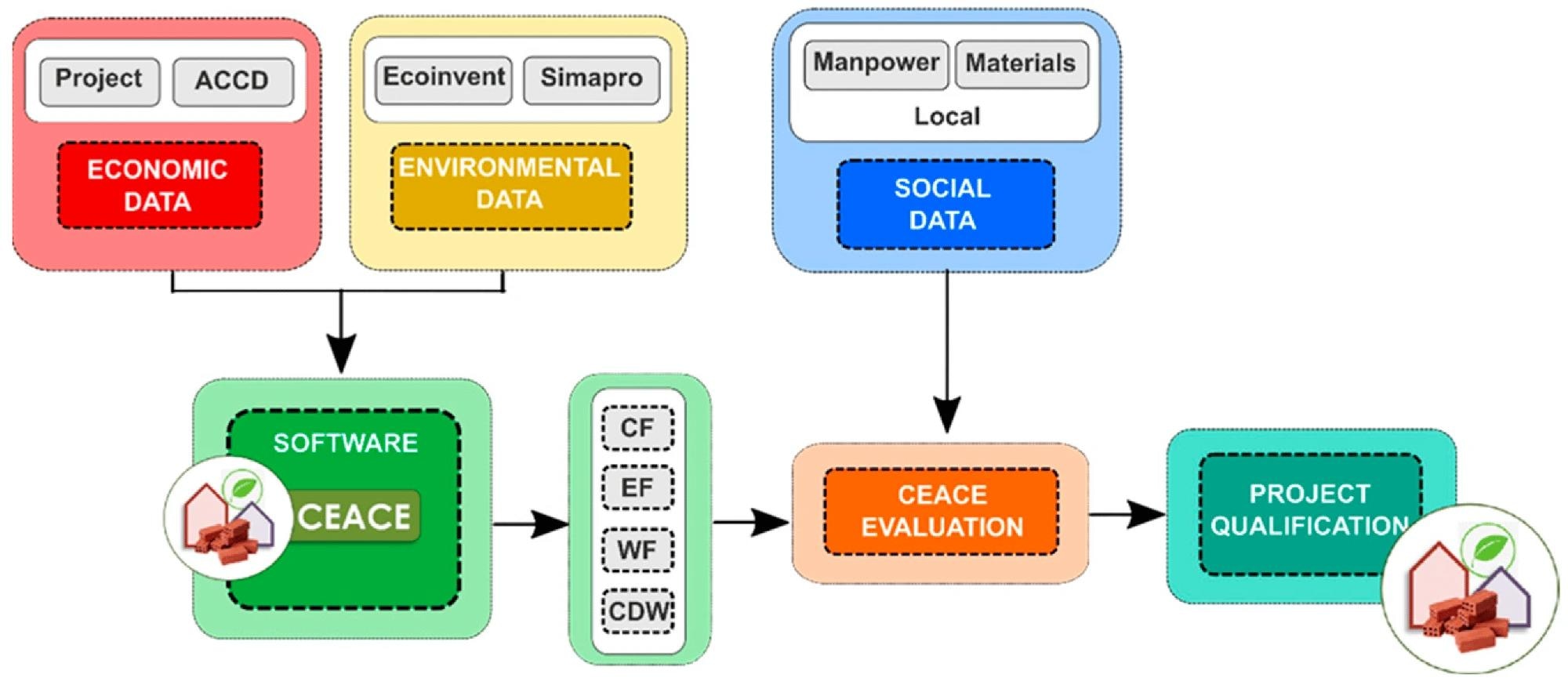 Methodology for obtaining CEACE evaluation by calculating the carbon footprint (CF), ecological footprint (EF), water footprint (WF), construction and demolition waste (CDW), and social data. Image Credit: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-5309/14/4/1131
Methodology for obtaining CEACE evaluation by calculating the carbon footprint (CF), ecological footprint (EF), water footprint (WF), construction and demolition waste (CDW), and social data. Image Credit: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-5309/14/4/1131
Buildings within the European Union (EU) play a significant role in energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and the extraction of raw materials and water, making an in-depth evaluation of their environmental footprint imperative. The EU's Circular Economy Action Plan highlights the critical need to diminish resource use and encourage the recycling of materials within the construction sector.
In response to these challenges, the authors of this study have introduced a novel methodology grounded in the Footprint Family concept aimed at enhancing sustainability in the housing construction sector of Andalusia.
Background
The environmental ramifications of the construction sector have catalyzed the development of sophisticated methodologies and tools aimed at a thorough evaluation of sustainability. Traditional life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies have been pivotal in analyzing environmental impacts across various stages of a building's life cycle.
Yet, to achieve a more comprehensive assessment, it is crucial to integrate additional indicators such as carbon footprint (CF), ecological footprint (EF), and water footprint (WF). These metrics broaden the scope of evaluation and provide a fuller picture of sustainability in construction projects. The authors underscore the necessity of utilizing methodologies and tools that are both accessible and effective in measuring and interpreting environmental impacts throughout a building's life cycle.
The Current Study
The methodology used in this research, the Andalusian Ecological Certificate for the Construction of Buildings (CEACE), presents a detailed framework for assessing the sustainability of residential projects in Andalusia. This approach incorporates a broad spectrum of environmental indicators, including CF, EF, WF, and the quantification of construction and demolition waste (CDW). By fusing these metrics with economic and social evaluations, the CEACE methodology aims to offer a comprehensive assessment of sustainability in residential construction.
The study utilized the CEACE method to analyze a total of 15 residential building projects, covering both single-family and multifamily dwellings ranging from one to ten floors. These projects were chosen to reflect a variety of construction solutions and typologies prevalent in Andalusia. The process entailed collecting and analyzing data on construction costs, CF values, EF values, and CDW quantities for each project to calculate the sustainability indicator I_CEACE.
This analysis facilitated a detailed comparison of environmental, economic, and social performance across the projects, allowing the researchers to discern sustainability trends and patterns influenced by different construction approaches and typologies. The findings provided deeper insights into the environmental impacts of residential buildings in Andalusia and pinpointed areas where improvements could enhance sustainability.
In addition to evaluating the environmental impact of the construction projects, the study also explored the impact of using Environmental Product Declarations (EPD) on sustainability assessments. By identifying construction units with significant environmental impacts, the research highlighted potential opportunities for integrating alternative materials with EPDs to reduce the projects' overall environmental footprints. This aspect of the study emphasized the importance of considering the life cycle impacts of materials and processes in sustainability evaluations.
Overall, the CEACE method has demonstrated its efficacy as a tool for advancing sustainability in residential construction projects in Andalusia. Its capacity to integrate diverse environmental indicators and provide a holistic assessment across multiple dimensions renders it both a practical and effective approach for gauging the environmental impact of building projects.
Results and Discussion
The study demonstrated the effectiveness of the CEACE method in promoting sustainability in residential construction projects. The analysis of the 15 projects revealed a range of costs, CF values, EF values, and CDW quantities, highlighting the diverse environmental impacts of different construction solutions.
Significantly, the study pinpointed construction units that exert the most substantial environmental impact. This identification facilitated the selection of alternative materials with EPDs to mitigate these impacts. The research also highlighted the sensitivity of the sustainability indicator I_CEACE to shifts in various parameters, reinforcing the need to consider different building typologies in future assessments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the research underscores the significance of the CEACE method for evaluating sustainability in residential buildings across Andalusia. By incorporating advanced indicators like EF and WF alongside traditional indicators like CF and CDW, this method offers a thorough assessment of the environmental, economic, and social dimensions.
The study's findings highlight the importance of considering the environmental impact of construction materials and processes and suggest avenues for further research, such as exploring reference values and integrating sustainability indicators into building information modeling. Overall, the research contributes valuable insights to the field of sustainable construction practices and provides a practical methodology for assessing the environmental impact of residential buildings.
Journal Reference
Solís-Guzmán, J., Garzón-González, P., González-Vallejo, P., & Marrero, M. (2024). Sustainability Evaluation of Residential Buildings Based on the Footprint Family: Application to Case Studies in Andalusia. Buildings, 14(4), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14041131, https://www.mdpi.com/2075-5309/14/4/1131